Contents
Steps for Jump Starting a Car
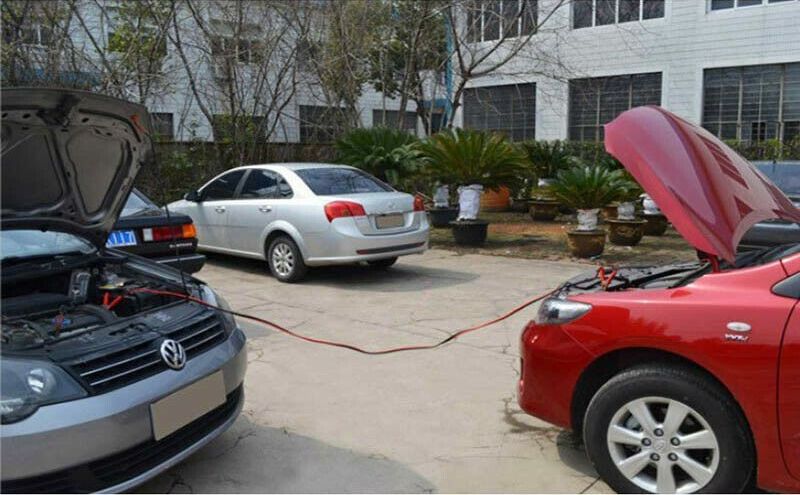

Make sure the batteries from the two cars are within reach of the cables.
Start by opening the hood and locating the battery. If you can’t find the battery, consult your owner’s manual. Its location can be surprising. For example, the battery is located in the rear of many hybrid gas-electric cars.
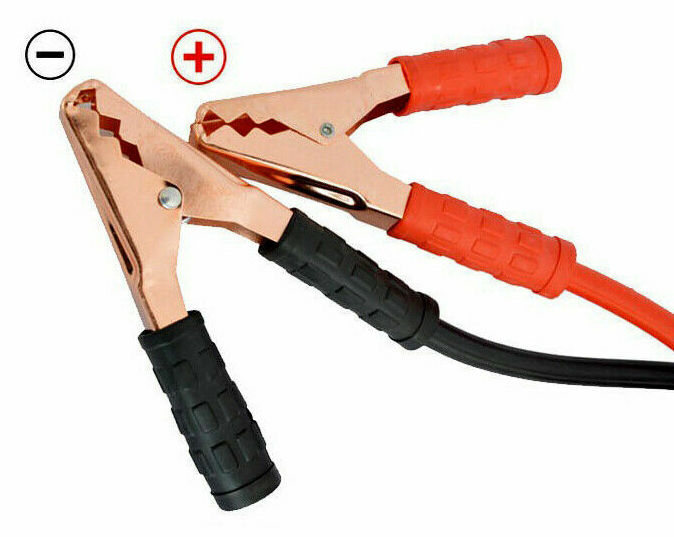
Remember—red is positive and black is negative.
All batteries have a positive post and a negative one. The positive post is marked with a plus sign (+) with an attached red cable/wire. There might be an insulated cover over the post. Likewise, the negative post will have a minus sign (-), and the cable should be black.
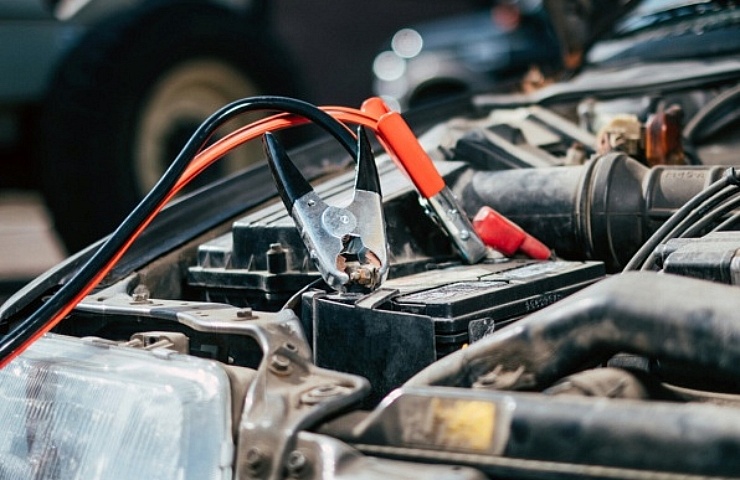
To start a car with a dead battery, you’ll need jumper cables and a good Samaritan with a running car. Position the two cars close to one another—but not too close. Do not let the cars touch.
Battery jumper cables are usually about 12 feet long—with two cables that have large clamps at each end. The ends are color-coded, red and black, so the cables are attached to the correct battery terminals.
The car with the good battery should have the engine off.
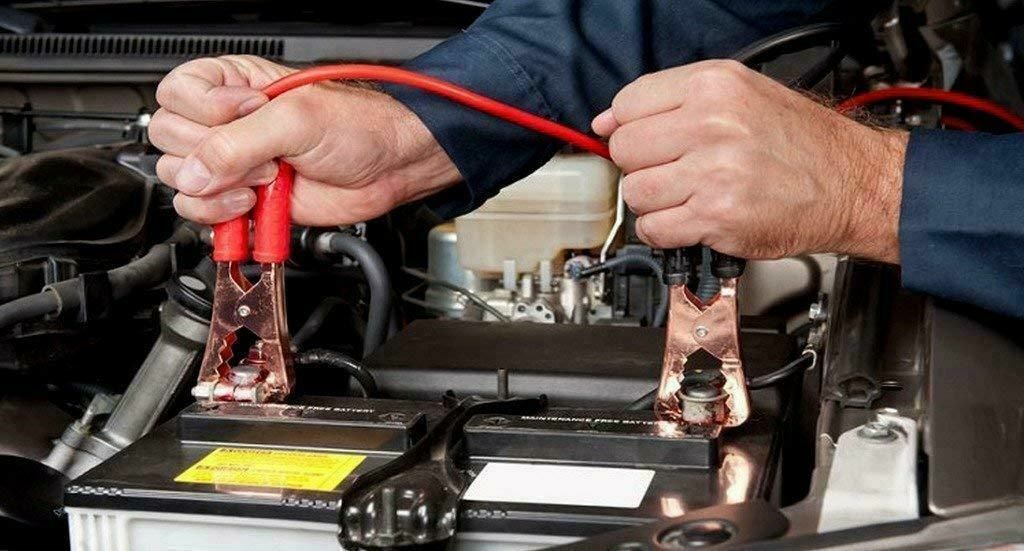

It is easy to connect the cables to the batteries.
Setup for the Jump Start

The clamps on the ends of the battery cables snap onto the battery posts.
- Put one red clamp of the jumper cable on the positive post of the dead battery. Connect the other red clamp to the positive post of the working battery.
- Connect the black clamp to the negative post of the working battery. And connect the other side of the cable with the black clamp to the negative post of the bad battery.
- Check that all the battery cables are clear of any moving parts.
What about attaching the negative cable to the ground?
That’s how many of us were taught to avoid sparks when jump starting—by putting the negative cable on an electrical ground far away from the battery on the dead car. It’s the official old-school ultra-safe way to jump start your car. However, many cables don’t have enough slack to reach a good ground, and you might not know how to find a suitable ground on the chassis. So, follow the steps outlined above, and it’s highly unlikely that you will create a spark.
It’s Time for the Jump
With the cables in place, start the car with the good battery and allow it to run for two to three minutes.
Now the exciting part. Start the car with the dead battery. It should fire up right away. If it doesn’t, allow the vehicle with the good battery to run for another five minutes and try again.
If your car is running, disconnect the cables in reverse order—first separating the black cable from the bad battery and then the good battery. Then, repeat with the red cable.
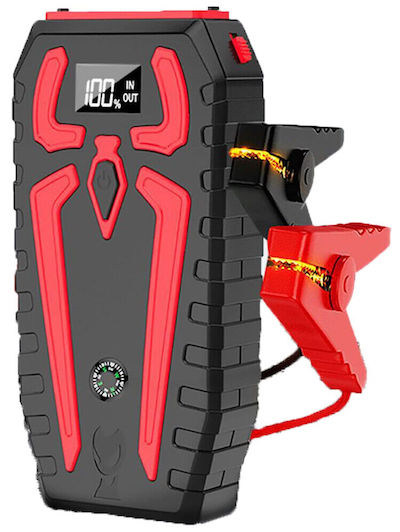
Shop now for jumper cablesUsing a Portable Battery Pack to Jump Start Your Car
Jumper cables have been the solution for starting an automobile for at least 100 years. The idea is that you connect your car’s dead battery to a good car battery, usually in another vehicle, and that provides the charge to start your car. The downside is that you need another vehicle to provide the power. That can be a problem if your car with a dead battery is on a lonely road.
Jumper cables are nearly obsolete today. The 1990s brought the first advance in portable jump start technology: jumper battery packs in an all-in-one enclosure. These chargers are powered by a sealed lead-acid or lithium-ion battery. They can also include accessories like an air compressor, flashlight, and a 110-volt inverter.
A portable jump start battery pack usually costs less than $50 and can be stored in your hatch or trunk. It’s a smart investment.
To use the portable charger, you usually have to first connect the cables into the battery pack. With everything in place, attach the pack’s red cable clamp to the positive post of the dead battery. Then connect the black clamp to the negative post of the dead battery. Many units have circuitry that flashes a light if the battery cables are not connected correctly.
- Set the battery pack in a safe place (like on the radiator support or on the fender), and turn it on.
- Start the car and then disconnect the battery cables immediately.
- Remove the black cable first and then the red cable.
- Turn off the battery pack.
Voila! You are now ready to drive.
Shop now for portable jumper packsTroubleshooting the Dead Battery
There are typically three reasons a battery won’t start the car:
- Battery failure – A battery has a finite lifespan. Heat and vibration will hasten the end of the battery. Typically a battery will last at least three years.
- Battery drain – If you inadvertently leave an accessory on after stopping the engine, the accessory could slowly use up the battery’s reserved energy. Check the usual culprits: headlights, a door ajar causing the interior lights to stay on, or even an open glovebox. Occasionally there might be a parasitic drain from a car component that is malfunctioning and drawing power from the battery.
- Alternator failure – The battery relies on the alternator to provide the bulk of the power demand when the car is running. It also provides power to recharge the battery. If the alternator doesn’t produce enough energy to recharge the battery, eventually the battery reserve will be drained.
Check out this article for more details on how to check for failures.
After Jump Starting Your Car’s Battery
Your previously stuck car is now running, which is fantastic. But there are things to do to ensure that the battery maintains its charge.
An essential step is to let the car run continuously for at least 20 minutes. This allows the vehicle’s alternator to charge the battery to a normal level.
If the battery was dead because you left the lights or other power components on, your battery and electric system should be back to normal.
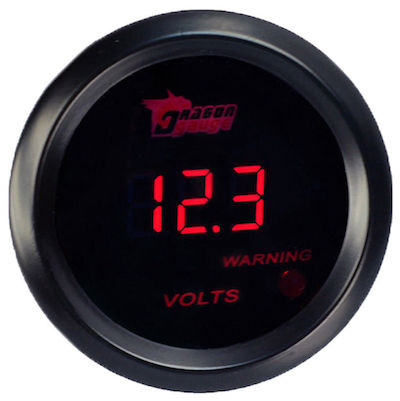
If you think the alternator is failing, the battery will not fully recharge. Most cars have a voltmeter on the gauge cluster showing the output of the alternator. If it shows less than 14 volts, that is an indication the alternator is not charging correctly. In that case, get your car to a mechanic or change out the alternator yourself. Depending on the condition of the battery and the failing alternator, you might be able to drive for 25 to 50 miles with a depleting battery.
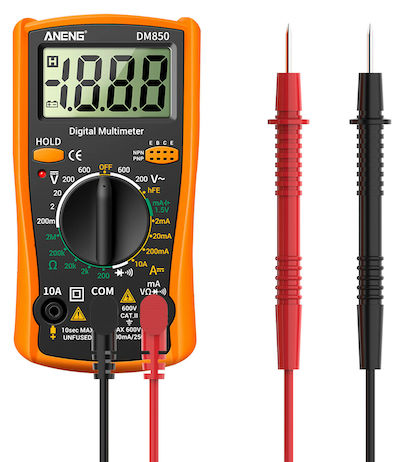
If you think the battery is failing, have it tested at an auto parts store or by your local mechanic. You can test it yourself with a multimeter. Turn off the car and place the multimeter’s leads on the battery posts. The battery should show at least 12 volts. If it is below that level, either the battery or alternator is likely bad.
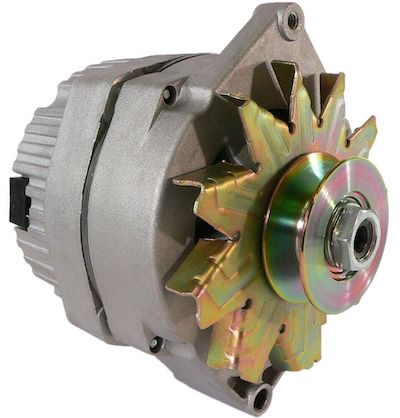
Alternator Woes
When a car engine is running, the alternator provides a steady power source to the electronics and for charging your battery. The alternator is so vital to your car’s health that a “check engine” light can illuminate if it malfunctions.
When your car doesn’t start, a primary culprit is the alternator. Here are a few signs that point to alternator woes.
- Did the dreaded “check engine” light come on? The alternator may not be providing sufficient power to the battery. (See our article: What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?)
- It could be the alternator if you smell an acidic odor under the hood. (Also see this: Why Does My Car Smell Like Eggs, Crayons or Other Odd Things?)
- Is your car taking more time to start? The battery might be losing power due to a bad alternator.
- If you notice the headlights flickering at night, especially when the car is idling, that’s another warning sign.
To test the alternator, with the multimeter still connected to the battery, start the car. The reading should increase to around 14 volts.
- If you see a reading above 16.5 volts, it is over-charging, which is also bad and a sign of a defective alternator.
- If you get a reading below 13.3 volts, the alternator is bad.
- If the reading is above 13.3 volts and the battery never gets to 12 volts (as tested above) after the engine runs for a few minutes, the battery is bad.
You can also ask a mechanic to check your electrical system.
How Much Does an Alternator Cost?
If you need to replace your alternator, you have three basic choices:
- You can buy a used alternator for about $75 to $200.
- A rebuilt alternator commonly costs between $100 and $200.
- A brand-new alternator ranges from about $150 to $400.